Technology
Principle
evapeos® technology uses the principle of Osmotic Evaporation.
In Osmotic Evaporation, water (or a solvent) transfers as a gas from the product toward an osmotic agent. These two miscible liquids are separated by a gas permeable membrane. The difference in activities between the two compartments results in a high gas flux at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Mass transfer occurs in three steps:

Vaporisation of water (or solvent) at the sample-air interface

Diffusion through the air-filled pores

Condensation at the air-osmotic agent interface
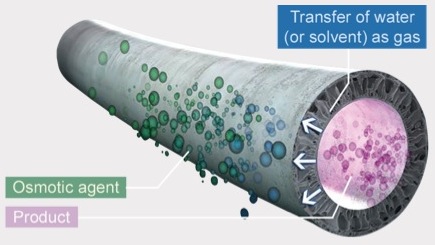
evapeos technology can be used for concentration (water removal) or solvent removal from aqueous solutions.
Note: Osmotic Evaporation is sometimes referred to as Osmotic Distillation.



